Table of contents
Originally published on DevDojo
Authentication is the most thing that a user does on a website, logging in or out, and it's necessary to take your application's authentication to the next level with password-less authentication. 🚀
This article will be covering how to take your application's authentication to the next level using Prisma and building an API for authentication!
Creating the API
Start by creating a new Next.js app:
npx create-next-app passwordless-authentication cd passwordless-authentication
After creating your Next.js app, it's time to create a new database, in this article, you'll use the free MySQL database provided by PlanetScale! 🔥
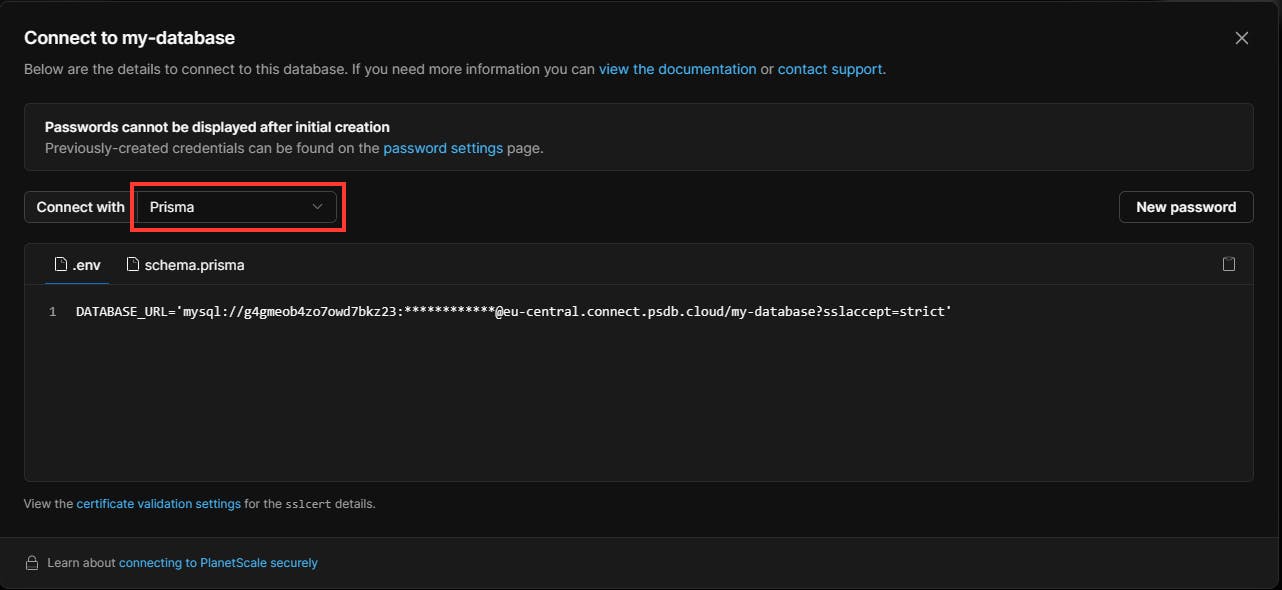
After you have created your database on PlanetScale, click on Connect and choose Prisma in the dropdown menu, copy both your .env and schema.prisma files.
Now, let's install Prisma in our Next.js app:
yarn add prisma @prisma/clientOnce done, let's initialize Prisma:
yarn prisma init
Now, replace the schema.prisma file located in prisma/schema.prisma with the schema you copied from PlanetScale, create a file called .env in the app's root and paste the .env file you copied too.
Finally, we have set up Prisma, we can start coding the actual API. 💙
First, let's create our model/table which defines what the things required for the user, add the following code to your schema.prisma:
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
code Int
status String
}
After that, run:
yarn prisma db push
Once your User table is ready, it's time to code our API, first, we have to create pages/api/newAccount.js file which will handle our new account creation:
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
export default function handler(req, res) {
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
const nodemailer = require("nodemailer");
const { email } = req.body;
// Check if the email is already in use
prisma.User.findUnique({
where: {
email: email,
},
}).then((user) => {
if (user) {
res.status(400).json({ error: "Email already in use" });
} else {
// Create reusable transporter object using the default SMTP transport
let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
host: "smtp.gmail.com",
port: 465,
secure: true, // Use SSL
auth: {
user: "someone@gmail.com",
pass: "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
},
});
// Generate a random 6 digit code
const code = Math.floor(100000 + Math.random() * 900000);
// setup email data with unicode symbols
let mailOptions = {
from: "someone@gmail.com",
to: email,
subject: "Passless Auth Demo",
text: `Your verification code is ${code}`,
html: `<b>Your verification code is <strong>${code}</strong></b>`,
};
// Send the email
transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, (error, info) => {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal server error" });
} else {
console.log("Message sent: %s", info.messageId);
// Respond with a message code sent
res.status(200).json({ message: "Code sent" });
}
});
// Save the user to the database on model User
prisma.user
.create({
data: {
email: email,
code: code,
status: "UNVERIFIED",
},
})
.then((user) => {
// Respond with a message code sent
res.status(200).json({ message: "Code sent" });
})
.catch((e) => {
console.log(e);
res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal server error" });
});
}
});
}
First of all, we are importing the Prisma client and creating a new client and defining nodemailer which we will use with Gmail SMTP to send emails to our users with the verification codes.
After that, it will create a new random verification code and save the email and code into Prisma, we use the email provided in the POST request and check first if the email is already in use, if it is, we return an error to the user, if not, the code sends an email to the user, if sent, it responds with status 202 and if such error occurs, it logs the error in the console and responds with status 500 with Internal server error.
That's how the new account creation system works!
Now, we have to allow the user to login into their accounts, so we create a new file at pages/api/loginAccount.js:
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
export default function handler(req, res) {
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
const nodemailer = require("nodemailer");
const { email } = req.body;
// Check if there is a user with the email
prisma.user
.findUnique({
where: {
email: email,
},
})
.then(async (user) => {
// If there is a user with the email
if (user) {
// Send the user a verification code
// Create reusable transporter object using the default SMTP transport
let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
host: "smtp.gmail.com",
port: 465,
secure: true, // Use SSL
auth: {
user: "someone@gmail.com",
pass: "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
},
});
// Generate a random 6 digit code
const code = Math.floor(100000 + Math.random() * 900000);
// setup email data with unicode symbols
let mailOptions = {
from: "someone@gmail.com",
to: email,
subject: "Passless Auth Demo",
text: `Your verification code is ${code}`,
html: `<b>Your verification code is <strong>${code}</strong></b>`,
};
// Send the email
transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, (error, info) => {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal server error" });
} else {
console.log("Message sent: %s", info.messageId);
// Respond with a message code sent
res.status(200).json({ message: "Code sent" });
}
});
// Update the user code
await prisma.user.update({
where: {
email: email,
},
data: {
code: code,
status: "UNVERIFIED",
},
});
res.status(200).json({ message: "Code sent" });
}
// If there is no user with the email
else {
// Return an error
res.status(400).json({ error: "Email not found" });
}
});
}
First, we define our Prisma client and nodemailer, after that, we check if there is such a user with the email, if there is, we send the user an email with the verification code and update the database, if not, we return Email not found.
Finally, we have to allow the users to verify their accounts either to login in or create new accounts, so create a file called verifyAccount.js:
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
export default function handler(req, res) {
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
const { email, code } = req.body;
// Check the code
prisma.user
.findUnique({
where: {
email: email,
},
})
.then(async (user) => {
if (user) {
// If the user is already verified
if (user.status === "VERIFIED") {
res.status(400).json({ error: "Account already verified" });
}
// If the code is correct
else if (user.code === code) {
// Update the user status to verified
await prisma.user.update({
where: {
email: email,
},
data: {
status: "VERIFIED",
},
});
res.status(200).json({ message: "Account verified" });
}
// If the code is incorrect
else {
res.status(400).json({ error: "Incorrect code" });
}
} else {
res.status(400).json({ error: "No user found" });
}
});
}
Also, here we define only the Prisma client, and we check if the code is correct, so we get the user and check the code, if it is correct, we verify the account, if not we return Incorrect code, if there is no user, we return No user found.
Now, you are ready to run your API, but first, you have to install nodemailer:
yarn add nodemailer
yarn dev
Outro + Source Code
Finally, we are done with this project, we have used Next.js to create our API and used Prisma to interact with our MySQL database provided by PlanetScale.
GitHub Repo: Omar8345/passwordless-authentication/


